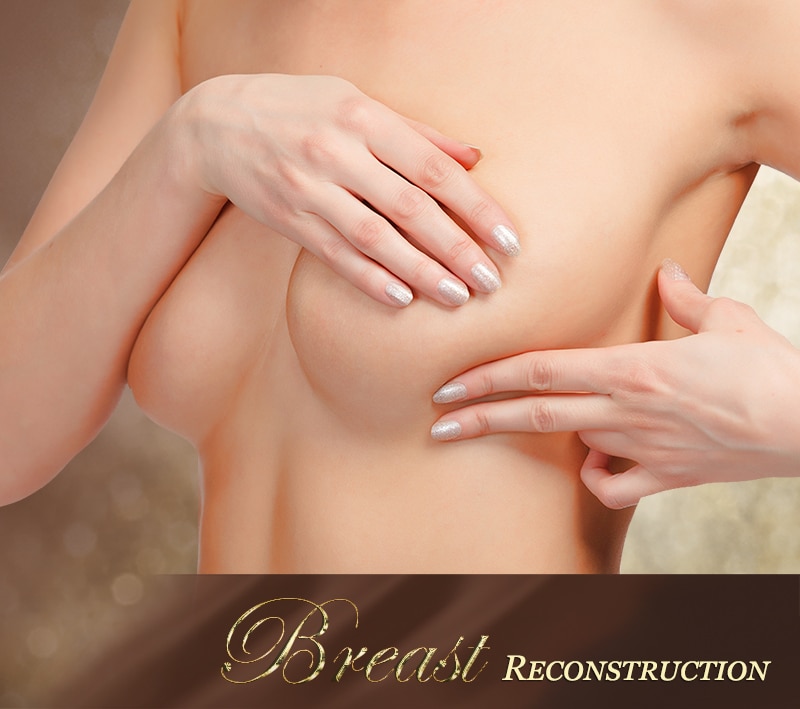
The DIEP flap technique is designed to take tissue from the abdomen to form a new breast mound. This microsurgical breast reconstruction technique allows patients to rebuild a natural-looking breast after mastectomy, while simultaneously undergoing a procedure similar to a tummy tuck.
You are an ideal candidate for DIEP Flap Reconstruction if you:
- Prefer the most realistic breast shape and texture
- Wish to utilize your own body tissue rather than implants
- Have a sufficient amount of tissue in the lower abdomen to create the new breast or breasts
- Are very physically active and wish to preserve your abdominal muscles
- Do not want or are not a candidate for implant reconstruction
- Have been previously radiated
- Are having immediate reconstruction at the time of skin sparing mastectomy
- Are having delayed reconstruction following mastectomy
- Would benefit from a “tummy tuck”
You are NOT an ideal candidate if you:
- do not have enough lower abdominal tissue to create the flaps
- have had previous abdominal surgical procedures such as tummy tuck (a C-section scar is usually ok)
- Are a smoker or quit smoking only recently
- cannot tolerate anaesthesia for long periods
- do not wish to have a lower abdominal scar
DIEP flaps are always free flaps. The flap (fat and overlying skin) survives on a blood supply via one or two perforators. Unlike the TRAM flap technique, in DIEP Flap surgery, preservation of the abdominal rectus muscles is possible because, during the preparation of the tissue, advanced microsurgical techniques are used to meticulously separate the tiny blood vessels that supply the skin and fat from the muscle while preserving muscular integrity. Once transferred to the chest, these tiny blood vessels of the DIEP flap are connected to existing blood vessels either at the side of the breastbone or in the armpit.
When the blood vessels of the flap are connected and the flap is seen to be receiving a good blood supply through the new channels, the skin and fat of the DIEP flap are shaped to form the new breast mound and the wounds are closed, generally with dissolving sutures. Whenever possible, a sensory nerve in the DIEP flap is connected to a sensory nerve at the mastectomy site to help maximize return of sensation in the reconstructed breast.
Because perforators are used (rather than the main deep inferior epigastric artery and vein) this breast reconstruction operation is not suitable for all women. Perforators are generally smaller in diameter than the main vessel, and vary in size between different people. If the perforators are too small, this type of reconstruction cannot proceed, as the risk of flap failure due to inadequate blood supply is too great. In fact, it is often not possible to predict the size of these vessels until surgery is underway, so your surgeon may offer you a DIEP flap reconstruction with the proviso that the operation may be changed to a free TRAM flap reconstruction on the operating table.
The procedure generally takes anywhere from six to eight hours to complete, and is performed under general anaesthesia. It is lengthy due to the precise nature of this microsurgical procedure. However, the surgical effort is rewarded by excellent cosmetic results. The procedure is also less invasive, resulting in less pain and faster recovery.
Although they are well hidden, scars from this reconstruction are long. In addition to the breast scar, there is a scar across the entire width of the abdomen at the bikini line, similar to that of a tummy-tuck, which can generally be concealed in most clothing.
A few months after the breast reconstruction procedure, if it was removed with mastectomy, restoration of the nipple and areola will follow. The shape of the breast may also be refined to be more symmetrical with your untreated breast. For many patients the reconstructed breast may be firmer and have a more youthful appearance than their natural breasts.